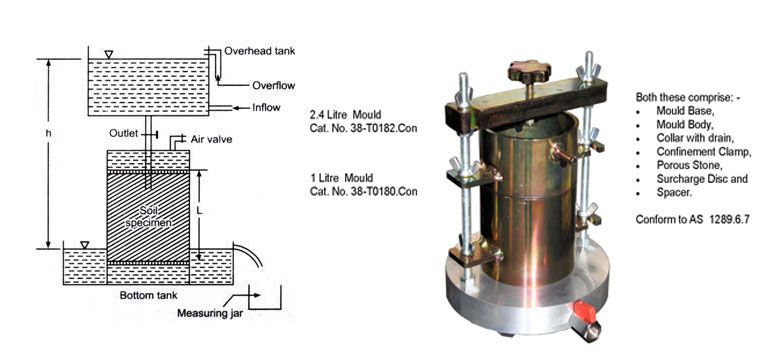
Permeability of Soil by Constant Head Permeameter
Objective: Assessment of Permeability of Soil by Constant Head Permeameter. Theory: The coefficient of permeability is equivalent to the degree of flow of water from a unit cross segment area underneath a unit hydraulic gradient. In the unimould head permeameter, the head inducing flow from the sample becomes constant during the experimentation. The coefficient […]
Read More →