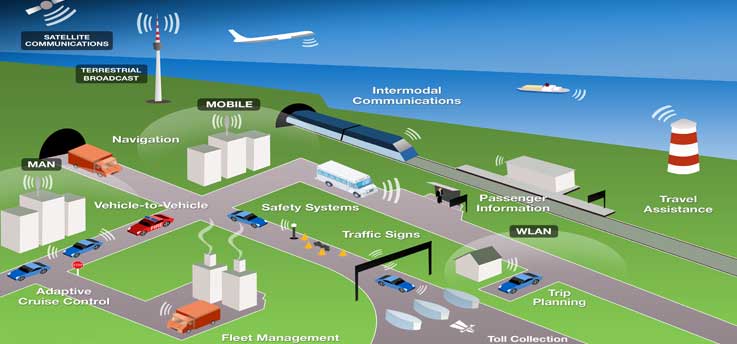
Why do we need Intelligent Transportation System (ITS)?
- Traffic overcrowding. Inadequate road development-increasing number of automobiles
- Low speed, bigger accident rates, amplified fuel consumption, and amplified pollution.
- Not possible to construct adequate new roadways or to meet new demands.
- These investigate the concept that treats highway systems and automobiles which make usage of them as incorporated system. Within them is the feature of Intelligent Transportation Systems.
- The aim of the ITS is to advance the transport system to make it additional efficient and safe by use of information, connections and control strategies.
India is moving through a period of enormous change in the area of transportation due to:
- Fast growing economy
- Inadequate and insufficient transportation system
- Growing automobiles ownership levels
What is Intelligent Transportation System?
- Intelligent transportation system (ITS) has a large number of technologies and strategies, comprising of information processing, communications, electronics and control.
- Incorporating these technologies and strategies to our own transportation system will help to save lives, save time, and save money as well
ITS Architechture:
Outline for planning, defining, and incorporating intelligent transportation system.
Advantages of Architecture
- Decreases time and resources taken to incorporate the technologies to local needs
- Helps recognize organizations and jurisdictions & search their active participation
Benefits of it’s applications:
- lessening in stops and setbacks at intersections
- Speed control & enhancement
- Travel time development
- Competence management
- Accident occurrence management
Framework:
# Communication System
- Efficient and competent operation of transit systems depends on the communications infrastructure and automobiles-based communications technologies and strategies.
- Communications systems are used to pass on voice and data among the transit vehicles and operation hubs, and to transfer commands among the operators and technologies.
- Transit communications systems mostly consist of the wireless technologies and applications.
# Fleet Management and Operations
- These incorporate different technologies which mostly are connected in different software packages, which permit the combination of various transit functions.
- GIS permit transfer agencies to precisely track where demand is situated in their service area.
# Fleet Management System
Usage of ITS:
1. Electronic Toll Collection
- Around the clock services and separate traffic management
- Electric payment through means of smart cards to encourage prompt passage through toll lanes
2. Global Positioning System
A proper system of computers, satellites, and receivers in which traffic data is included in the map, the driver can get the most convenient route, will know about the position of the signals ahead, predict about potential traffic jams, etc.
Advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages
- Travel to locations which we don’t know using the most convenient route
- Will never get lost
- Find hospitals, eateries and highways
- Usage of traffic flow data to analyze the traffic situation
Disadvantages
- Extra cost for installation
- Scarce availability of intricate map for all areas
- Inconsistency b/w indicated and local names
- Inadequate traffic information analysis to analyze traffic conditions
3. Advanced Traveler Information
- It contributes to save the travel duration, diminish cost dependability, extra comfort to travelers, augments travel safety and security.
- The information which the passengers need are of dynamic and static. Static information incorporates routes and timetables. While dynamic information contains, traffic conditions,real-time transit timetables, incidents and accidents, weather, parking availability etc.
- Transportation Management Centers reacts to the real-time traffic conditions, control which lanes may be used, traffic signal timing
4. In-automobile Transit Information System
- Announce stops, shift possibilities, based on the automobile’s location, route, and direction, and time taken for travel.
- Information through variable message signs located at one or additional places in the bus.
- Firstly aggravated by support for the disabled, useful for those new with the route, when the bus is packed, and when it is hard to see outside the vehicle.
- Gives news and Weather, video clips, and other travel and road related information on the flat-panel display.
5. Automatic Passenger Counter
- The APC robotically reports the number of travelers, time and destination of each stop as passengers get on and off the vehicle.
- The APC can gather data, with a lessening in time, cost, and attempt by ways of infrared beams at the doors
- With the information given by the APCs, transit planners can make alternations to routes and timetables that better serve the transportation needs and services of their locality
Advantages of ITS
- Improvised safety services
- improvised traffic flow
- Lessened travel cost
- Good environmental quality
- Augmented business activity
- Higher user acceptance
- Improved travel information
- Improved planning information
Disadvantages of ITS
- Hard to apply in mixed traffic
- Prelude difficulties in understanding
- ITS equipments are expensive
- The control system software could be hacked and misused