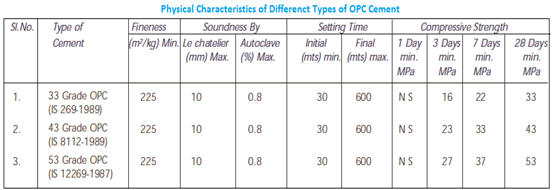
Soundness of Cement
Objective: To assess the soundness of cement by Le-chatelier Method Apparatus Le chatelier mould The mould comprises of a very minute split cylinder made out of spring brass or some other compatible metal of 0.5mm density creating of a mould 30mm interior diameter and 30mm height. On both sides of the split, they are joined […]
Read More →