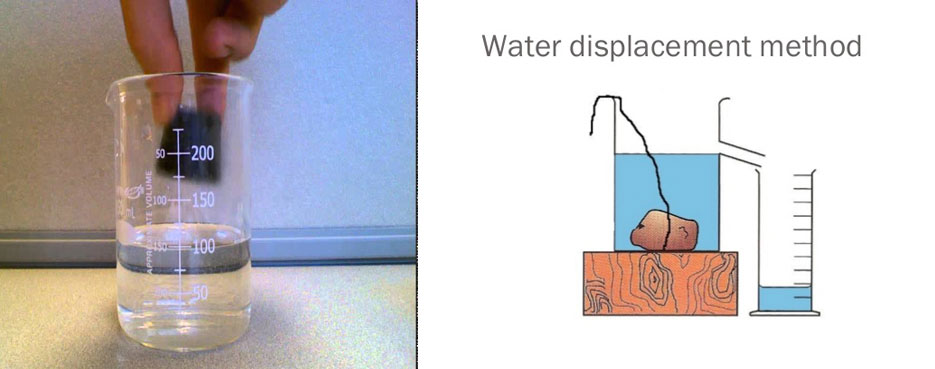
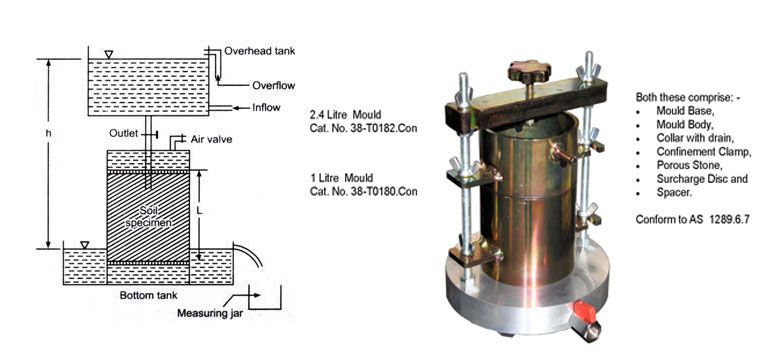
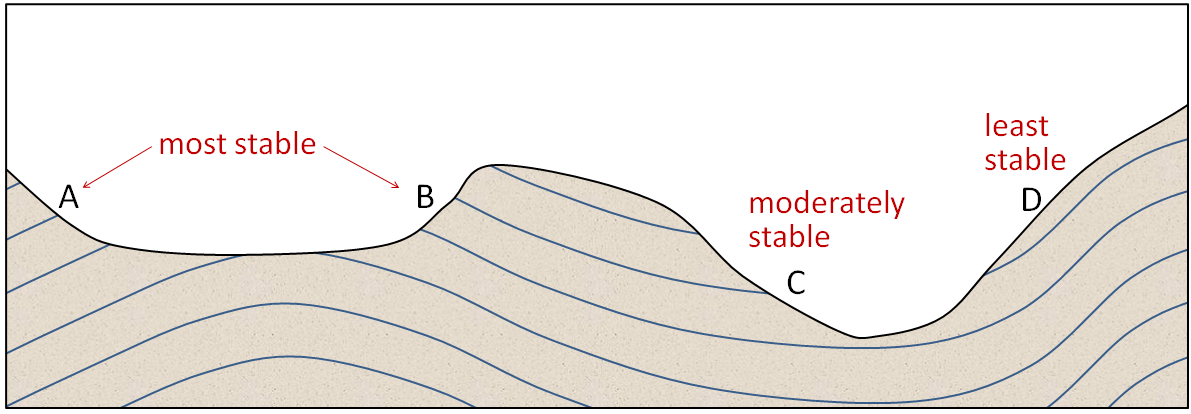
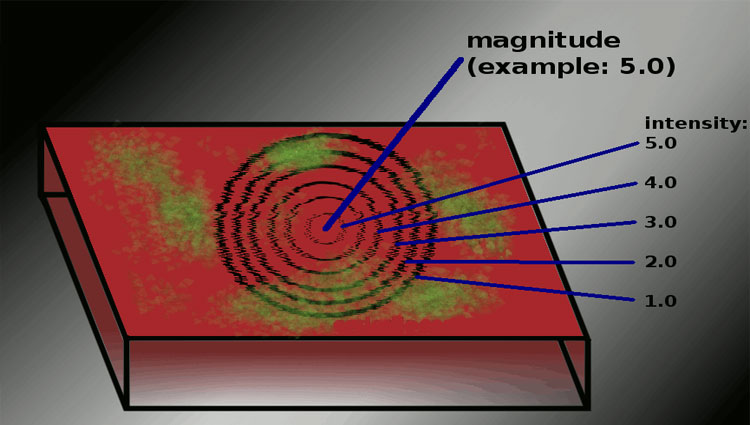
Design of Raft Foundation
Design Considerations of Raft or Mat Foundation: In those cases, where the load transmitted by the columns in a structure are so substantial or the reasonable soil pressure so little that individual footings would cover more than around one-portion of the region, it might be ideal to give a persistent footing under all columns, wall […]
Read More →