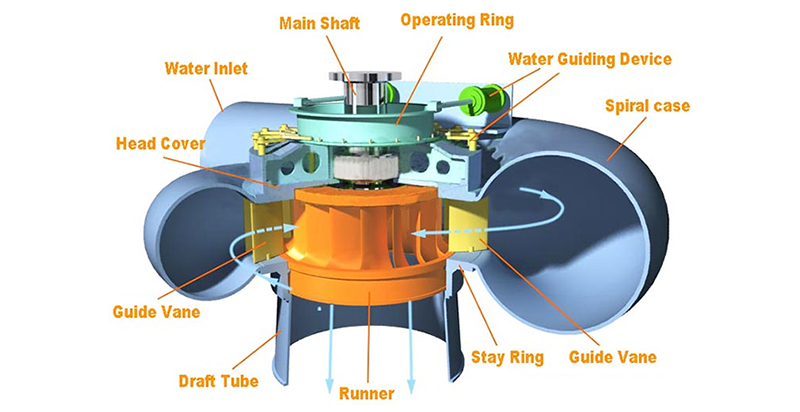
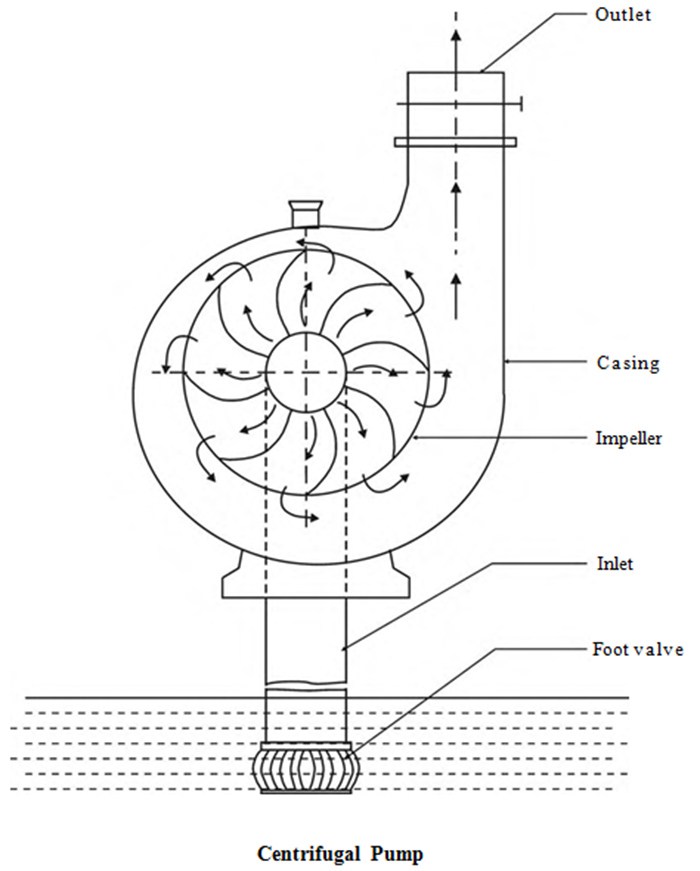
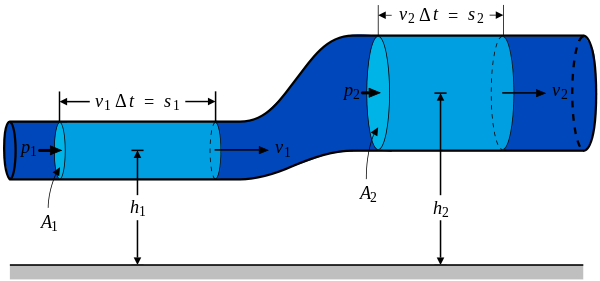
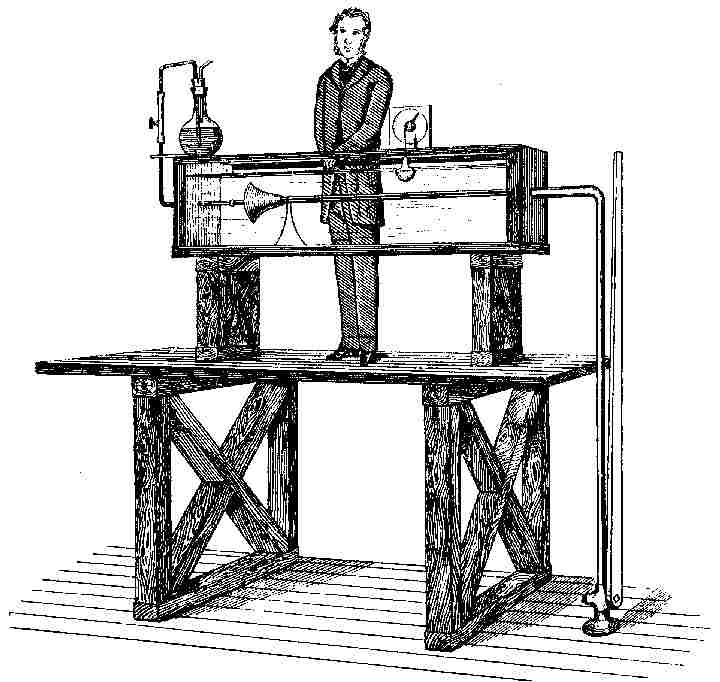
Reciprocating Pump
Reciprocating pump refers to the positive displacement pump. The provided pump is solitary acting single cylinder pump comprising of an air vessel. It could be utilized for minimum discharge at greater heads. Preparing is not compulsory since it is a positive displacement pump. Reciprocating pumps are utilized in pumping water in hilly regions. Reciprocating pumps […]
Read More →